经典课题:常见病的少见表现,及基于机制的新疗法研发;美国133项在研狼疮基金,关注于这些热点(2024)
2024-10-15 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研
本文介绍狼疮特点及未解决临床问题,梳理美国 NIH 在研狼疮项目,包括获资助者、研究热点等,分享课题摘要,为狼疮研究提供启发。
狼疮(Lupus)也称为系统性红斑狼疮(Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE),是一种复杂的自身免疫性疾病,其特点是免疫系统错误地攻击身体的自身组织,导致广泛的炎症和组织损伤。该病可影响多个器官系统,包括皮肤、关节、肾脏、心脏和神经系统。
尽管近年来在狼疮的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在一些重要而未解决的临床问题:
-
治疗个体化:由于狼疮表现形式多样,患者对治疗的反应差异很大,目前仍缺乏足够的个体化治疗方案来有效控制所有患者的疾病活动。
-
长期管理:虽然现有药物可以控制症状和延缓疾病进展,但许多患者长期使用这些药物会有严重的副作用。因此,开发更安全、更有效的长期治疗策略是一个重要的未解决问题。
-
疾病标志物:缺乏可靠的生物标志物来监测疾病活动和预测疗效,这限制了对疾病进展的及时干预。
-
早期诊断:由于早期症状往往非特异性,狼疮的早期诊断是一个挑战。早期诊断对于预防严重并发症和改善长期预后至关重要。
狼疮的研究仍在持续进行,科学家们正在探索新的治疗目标和策略,以提高治疗效果和患者的生活质量。未来的研究需要继续深入了解狼疮的病理机制,开发新的药物,并改善疾病的管理策略。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研狼疮相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Lupus”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对狼疮的在研有133项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
1,在研狼疮基金最多的PI
-
FEINSTEIN INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL RESEARCH 的 DIAMOND, BETTY
-
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF ARTHRITIS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL AND SKIN DISEASES 的 HASNI, SARFARAZ
-
BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENTER 的 TSOKOS, GEORGE C
-
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 的 IZMIRLY, PETER
-
WEILL MEDICAL COLL OF CORNELL UNIV 的 PASCUAL, MARIA VIRGINIA
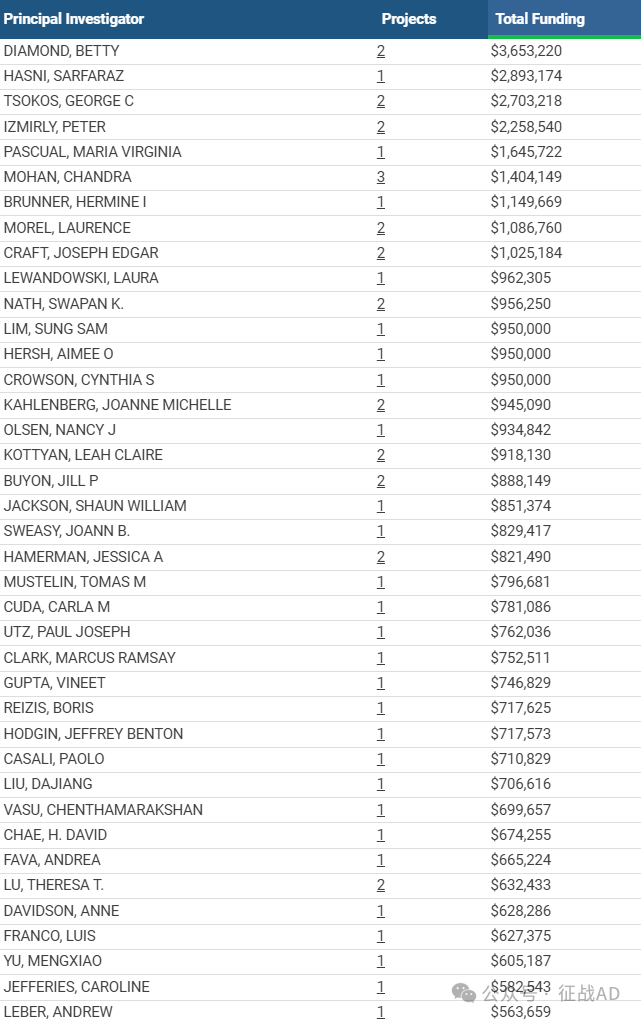
2,狼疮基金最多的研究机构
-
费恩斯坦医学研究所
-
国家关节炎和肌肉骨骼及皮肤疾病研究所
-
纽约大学医学院
-
杜克大学
-
贝思以色列女执事医疗中心等
二,狼疮研究热点是什么?
狼疮研究领域总览(根据关键词)
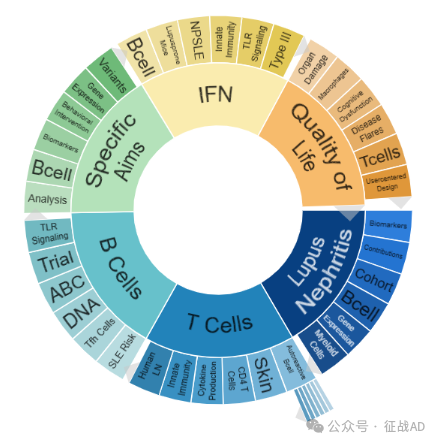
A,关于狼疮性肾炎(Lupus Nephritis)的研究项目最多
有 35 项在研基金涉及到了狼疮性肾炎,关注最多的方面包括生物标志物(Biomarkers)、贡献(Contributions)、队列(Cohort)、B细胞(B Cell)、基因表达(Gene Expression)、髓系细胞(Myeloid Cells)等研究。

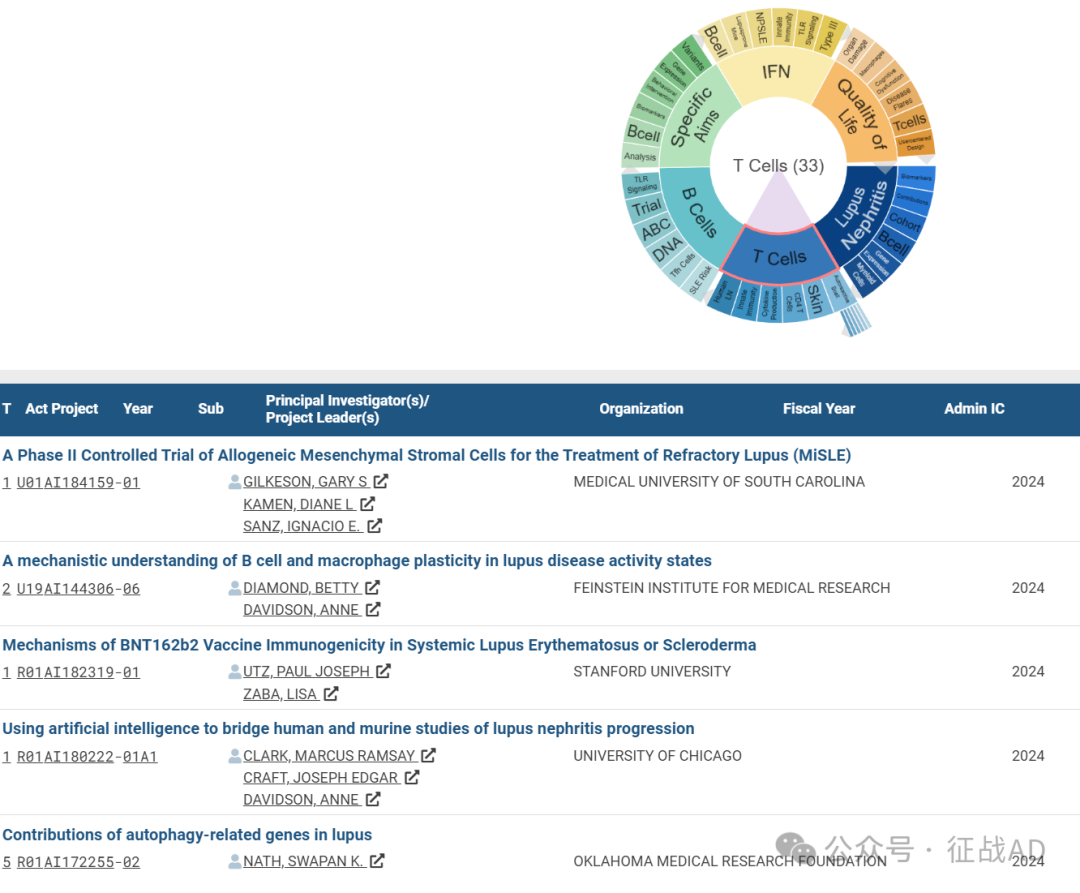
B,关于T细胞(T Cell)的研究项目
有 33 项在研基金涉及到了T细胞,关注最多的方面包括自身反应性B细胞(Autoreactive B Cell)、皮肤(Skin)、CD4 T细胞、细胞因子产生(Cytokine Production)、先天免疫(Innate Immunity)、人狼疮(Human LN)等研究。
C,关于B细胞(B Cell)的研究项目
有 30 项在研基金涉及到了B细胞,关注最多的方面包括SLE风险(SLE Risk)、滤泡辅助T细胞(Tfh Cell)、DNA、实验(Trial)、TLR信号(TLR Signaling)等研究。

其他狼疮研究大的方向也包括具体目标(Specific Aims)、生活质量(Quality of Life)、IFN等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在狼疮领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,Anti NMDA Receptor antibodes in adult brain dysfunction and fetal brain development: lessons from lupus
We have developed a mouse model in which we have now shown that DNRAb, when they penetrate the hippocampus, cause acute neuronal death subsequently leading to persistent microglial activation, neuronal dendritic loss, and cognitive impairments. Suppression of microglial activation by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors leads to a restoration of neuronal integrity and cognitive function. Using the same model, we have demonstrated that maternal DNRAb cause death of female fetuses and cognitive impairment in male offspring through transplacental transport. We have demonstrated in subjects with SLE that memory impairment is associated with increased titers of DNRAb and that a reduced microstructural integrity of parahippocampal fibers also associates with DNRAb.
We proposed to continue to study both the mouse model and SLE patients, to understand the mechanisms of microglial activation and how ACE inhibitors restore neuronal integrity. We will determine how DNAbs alter male and female fetal brain development. We will assess microglial activation and loss of blood brain barrier integrity in SLE patients and the association of these abnormalities with elevated titers of DNRAb. These studies have already led to a funded clinical trial of ACE inhibitors in non-focal central nervous system manifestations of NPSLE, and have the potential to reveal additional potential therapeutic strategies.
B, Lupus nephritis: novel insights in the pathogenesis and treatment
This proposal will test the hypothesis that interaction of constituents of the immune system with kidney resident cells and the ectopically formed high endothelial venules, determines the development of inflammation and injury in the setting of LN. Corollaries of this hypothesis are that kidney resident cells can serve as gateways for the administration of targeted therapeutics for the treatment of LN and that kidney tissue pathology can be recorded with high fidelity in the urine cells of patients with LN.
There are 2 projects in this proposal: 1) Interplay between autoimmune effectors and kidney resident cells in lupus nephritis and 2) Newly formed high endothelial cells in the kidney- pathogenesis and implications in lupus nephritis.
The proposal will be supported by 3 cores: The Administrative Core will be responsible for regulatory compliance, budget management, scheduling meetings. The Nanoparticle Immune Delivery Core will be responsible for the construction of nanoparticles loaded with drugs and biologics and tagged with antibodies for cell-specific delivery. The Single Cell, Spatial Transcriptomics and Bioinformatics Core will perform single cell transcriptomics studies and will provide statistical and bioinformatics support. This proposal through extensive synergistic plans between the project leaders brings forward novel and significant elements in the study of the pathogenesis, treatment and biomarker development in patients with LN.
作者:Hanson临床科研
版权声明:
本网站所有注明“来源:梅斯医学”或“来源:MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明“来源:梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,本网所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,转载内容不代表本站立场。不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言










#系统性红斑狼疮# #生物标志物#
70