精神分裂症,美国在研的184项基金简述(2024)
2024-09-20 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研精神分裂症相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
精神分裂症(Schizophrenia)是一种严重的长期精神障碍,表现为思维、感知、情绪、行为和自我意识的显著扭曲。患者可能经历幻觉、妄想、思维混乱、以及情感平淡等症状。
尽管有药物和心理社会干预可以有效缓解症状,但依旧存在许多未解决的临床问题:
-
早期诊断的挑战:精神分裂症在早期往往缺乏明显的临床症状,导致许多患者在确诊时已经处于疾病晚期。如何提高早期诊断的准确性和效率,是当前面临的一个重要问题。
-
治疗响应差异:尽管抗精神病药物可以有效控制精神分裂症的某些症状,如幻听和妄想,但许多患者对当前的药物治疗反应不佳,尤其是对认知障碍和负性症状。
-
药物副作用:现有抗精神病药物常见副作用包括运动障碍、体重增加、代谢综合症等,这些副作用可能严重影响患者的生活质量和治疗依从性。
-
社会和职业功能:即使症状得到控制,许多患者的社会功能和职业功能仍然受限,这部分是由于疾病本身的特点,部分也是由于社会对精神病患者的偏见和歧视。
-
早期诊断和干预:精神分裂症的早期诊断和干预是提高预后的关键,但早期识别和干预策略的有效性仍需进一步研究和优化。
精神分裂症的治疗和管理是一个复杂的挑战,需要综合药物治疗、心理社会干预及患者和家庭教育等多种策略。未来的研究需要继续探索更有效的治疗方法,减少药物副作用,并改善患者的整体生活质量。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研精神分裂症相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Schizophrenia”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对精神分裂症的在研有184项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
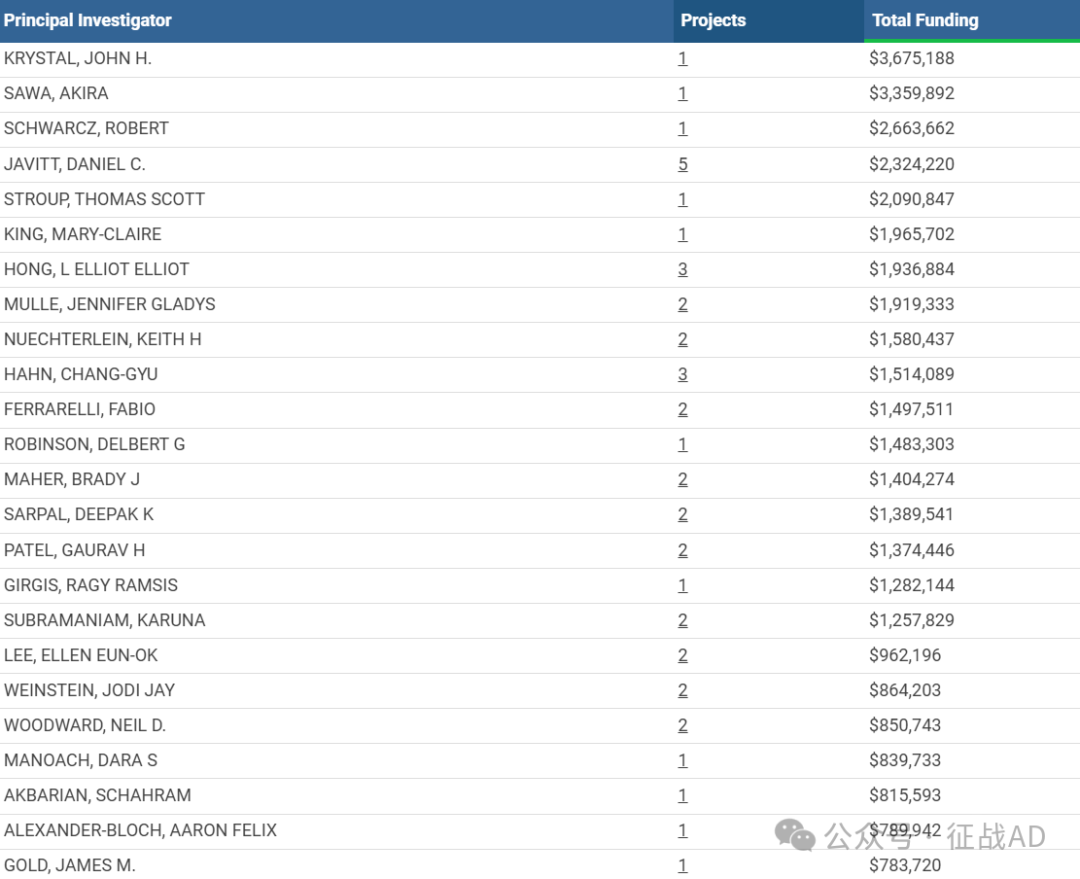
1,在研精神分裂症基金最多的PI
-
YALE UNIVERSITY 的 KRYSTAL, JOHN H.
-
JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY 的 SAWA, AKIRA
-
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE 的 SCHWARCZ, ROBERT
-
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES 的 JAVITT, DANIEL C.
-
NEW YORK STATE PSYCHIATRIC INSTITUTE DBA RESEARCH FOUNDATION FOR MENTAL HYGIENE, INC 的 STROUP, THOMAS SCOTT
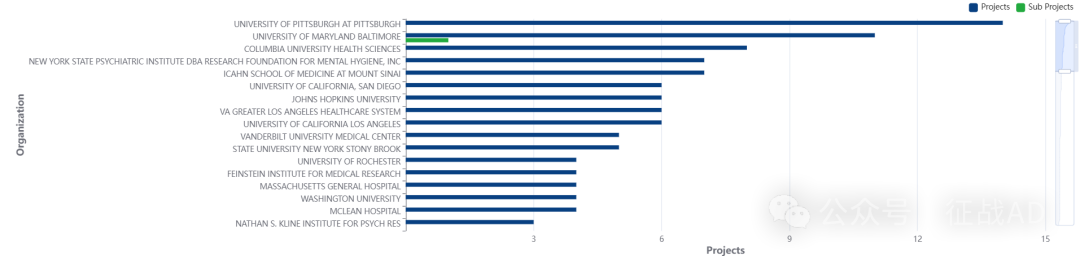
2,精神分裂症基金最多的研究机构
-
匹兹堡大学匹兹堡分校
-
布莱根妇女医院
-
纽约州精神病研究所 DBA 心理卫生研究基金会
-
马里兰大学巴尔的摩分校
-
西奈山伊坎医学院等
二,精神分裂症研究热点是什么?
精神分裂症研究领域总览(根据关键词)
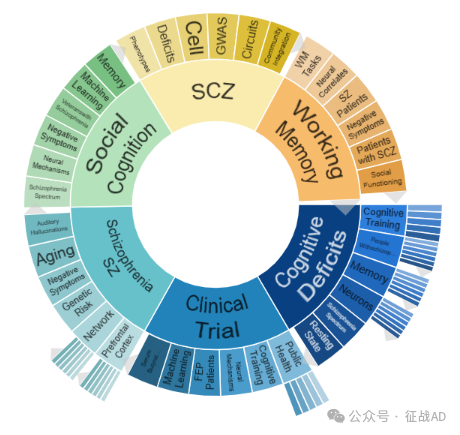
A,关于认知缺陷(Cognitive Deficits)的研究项目最多
有 49 项在研基金涉及到了认知缺陷,关注最多的方面包括认知训练(Cognitive Training)、精神分裂症患者(People with Schizophrenia)、记忆(Memory)、神经元(Neurons)、精神分裂症谱系(Schizophrenia Spectrum)、静息态(Resting State)等方面研究。

B,精神分裂症(Schizophrenia SZ)的研究
有 47 项研究涉及到精神分裂症,研究领域主要涉及听觉(Auditory)、衰老(Aging)、阴性症状(Negative Symptoms)、遗传风险(Genetic Risk)、网络(Network)、前额叶皮质(Prefrontal Cortex)等方面研究。
C,临床研究(Clinical Trials)
有 37 项研究涉及到临床研究,涉及的关键词包括公共卫生(Public Health)、认知训练(Cognitive Training)、神经机制(Neural Mechanisms)、FEP患者(FEP Patients)、机器学习(Mechine Learning)、血清丁酸水平(Serum Butyrate Levels)等。

其他精神分裂症研究大的方向也包括社会认知(Social Cognition)、SCZ、工作记忆(Working Memory)等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在精神分裂症领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,Clinical Trial Data Processing, Analysis, and Coordination Center (CT-DPACC) for Accelerating Medicines Partnership Schizophrenia (AMP SCZ) Project
In response to these challenges, in 2020, the NIMH launched the Accelerated Medicines Partnership® Schizophrenia (AMP® SCZ) project, a large, observational study designed to de-risk the drug development process through validation of drug development tools, including biomarkers related to cognition, brain structure and function, fluid biomarkers, genetic vulnerability and communication. Investigators in the current proposal led the Data Processing, Analysis and Coordination Center (DPACC) for the AMP SCZ project to manage and coordinate data from the clinical networks, overseeing all aspects of data flow, quality assurance, processing, and analysis.
The current proposal is in response to RFA-MH-24-151, the next phase of the AMP SCZ project, to perform Proof of Principle (PoP) clinical trials utilizing Phase 2 ready compounds to target pathophysiologically relevant mechanisms that have the potential to produce a detectable signal (change) in biological, digital, cognitive, or clinical outcome measures within a 12-16 week period of study. We propose the Clinical Trial DPACC (CT-DPACC) to provide executive management, direction, and overall coordination, including data processing and analyses of data for the PoP trial(s). We will maintain the current research team and organizational structure and augment it with a strong regulatory team, including a contract research organization, to support investigational new drug submission(s) and perform regulatory and safety monitoring.
Our specific goals are (1) offer study design and regulatory support, (2) manage, direct, monitor, and coordinate the multi-site clinical trials, and (3) develop data operation procedures, biostatistics, and data analysis. Successful completion of the CT-DPACC project, in conjunction with the supported PoP clinical trials network, is expected to yield clinically validated compounds for CHR.
B, Prostate inflammatory lesions as a proving ground for development of aggressive prostate cancer
For the RAISE initiative, we developed the NAVIGATE model of coordinated specialty care (CSC) for first episode psychosis which supports the EPINET goal of furthering measurement-based care and shared treatment decisions. To meet the EPINET goal of improving treatment, having all sites providing treatment using the same model has distinct advantages. Therefore, we have engaged 11 NAVIGATE sites in 4 states, enabling us to address challenges in different regions and find solutions that are not dependent on the environment and support of a single state. Based on our experience training NAVIGATE sites and analyses of RAISE-ETP data, we have identified targets for improvement of services.
Our specific targets for improvement divide into two categories. First, initial approaches added to NAVIGATE care for all participants to provide an enhanced version of NAVIGATE (E-NAVIGATE). Second, three research projects target critical junctures in CSC care.
Study 1 aims to reduce duration of untreated psychosis (DUP). In RAISE-ETP median DUP was 74 weeks and had a significant impact on quality of life and symptoms. We will study the effect of targeted ads that appear in response to specific terms when someone searches the internet. We expect that this will increase the number of young people who will come to our clinics with shorter DUP.
Study 2 addresses further reduction of hospitalization. Even with CSC, approximately one third will be hospitalized within 2 years and poor adherence to medication can lead to hospitalization. Direct observation of treatment can substantially improve adherence and reduce hospitalization. We will study a unique suite of methods for direct observation delivered as an app on a smart phone to support adherence. In a randomized trial we will compare this intervention to usual E-NAVIGATE to improve adherence and reduce hospitalization.
Study 3 is designed to identify E-NAVIGATE participants who are at high risk for disengagement, and to intervene in order to prevent/delay disengagement because even with CSC, 30-50% of participants will disengage from treatment within 2 years. We will compare an internet delivered version of E-NAVIGATE that reduces treatment burden to usual clinical strategies to prevent disengagement. We will build upon our RAISE-ETP and post-ETP experience to build a unique network that will deliver an evolving CSC that changes based upon feedback from experience and a dedicated informatics platform.
Research, designed to be generalizable not only to our network but to CSC practice more broadly, will set the stage for the next generation of CSC deployment.
作者:Hanson临床科研
版权声明:
本网站所有注明“来源:梅斯医学”或“来源:MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明“来源:梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,本网所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,转载内容不代表本站立场。不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言










#精神分裂症# #美国国立卫生研究院#
6